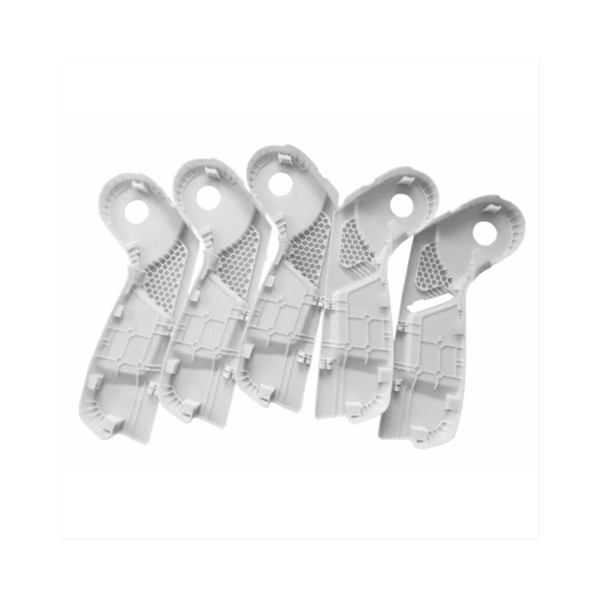
GD Prototyping

Rapid Prototyping 3D Printing
Rapid prototyping is the use of digital technologies to design and fabricate prototypes faster and easier.
Classification:
3D Printing
Keywords:
- rapid 3d printing
- rapid prototyping 3d
- 3d printing prototype service
- rapid prototyping 3d printing
- Description
- Specification
- Application
- FAQS
Rapid prototyping 3D offers significant advantages in modern product development by combining speed, flexibility, and broad applicability. One of the key benefits is speed and cost efficiency. Traditional prototyping methods often require weeks to produce a physical model. In contrast, 3D printing can create prototypes within hours or a few days. This dramatic reduction in time helps accelerate project timelines and allows you to move quickly from concept to testing. Additionally, rapid prototyping 3D eliminates the need for costly molds and tooling. This lowers upfront expenses, making it more accessible to test ideas and explore multiple designs without large investments.
Another major advantage of rapid prototyping 3D is design flexibility and iteration. Traditional manufacturing often limits how quickly you can make changes to a prototype once tooling is set up. With 3D printing, you can adjust digital models easily and produce updated prototypes quickly. This flexibility supports an iterative design process, where you test, gather feedback, and refine parts multiple times. The ability to rapidly customize designs enables more innovation, since you can explore complex geometries, internal structures, and customized features that would be difficult or expensive to achieve with conventional methods.
Rapid prototyping 3D also finds application across a wide range of industries. In aerospace, automotive, healthcare, and consumer products, the technology helps teams develop new parts and products faster while maintaining precision and quality. For example, aerospace engineers can prototype lightweight, complex components that meet strict performance requirements. Healthcare professionals use 3D printed models to create patient-specific implants and surgical guides. Consumer product developers benefit from the quick turnaround times that allow them to test form, fit, and function before moving to mass production.
The combination of fast production, adaptable design, and industry versatility makes rapid prototyping 3D a valuable tool. It supports efficient development cycles and helps you respond to changing demands and technical challenges effectively. This approach enables you to optimize designs early, reduce risks, and improve product outcomes across many applications.
| Parameter | Value / Description |
|---|---|
| Technology Type | 3D Printing Technology |
| Material | Engineering plastics |
| Use Case | Bridging pre-production prototypes and mass production |
| Production scale | From low volume to hundreds of thousands of parts |
- Product Design: Speeds up prototyping and design validation.
- Automotive & Aerospace: Enables rapid part and tooling prototyping.
- Medical & Healthcare: Creates custom models and surgical guides.
- Consumer Electronics: Rapidly prototypes parts and enclosures.
- Jewelry & Fashion: Allows quick creation of custom designs.
- Architecture & Construction:Provides scale models for design and presentation.
- Education & Research:Enhances hands-on learning with custom models.
- Industrial Manufacturing:Makes parts, jigs, and fixtures for testing.
- Entertainment & Media:Creates models and props for films and games.
1. What is rapid prototyping?
Answer: Rapid prototyping is the process of quickly creating a physical model or prototype from a digital design, usually through 3D printing technologies, to test form, fit, and function before production.
2. What are the benefits of 3D printing for prototyping?
Answer:3D printing enables faster development cycles, reduced costs, easy iterations, and the ability to create complex shapes that would be difficult or impossible with traditional methods.
3. What materials can be used for 3D prototyping?
Answer: Common materials include PLA, ABS, PETG, nylon, resin, and even metals like aluminum and titanium, depending on the specific printing technology used (FDM, SLA, SLS, etc.).
4. How accurate are 3D printed prototypes?
Answer:3D printing can achieve high precision, typically within 0.1mm to 0.2mm, depending on the printer and material used.
5. How long does it take to create a prototype using 3D printing?
Answer: The time can vary depending on the complexity and size of the design, but typical prototypes can be created in a few hours to a few days.