GD Prototyping

Metal Materials 3D Printing
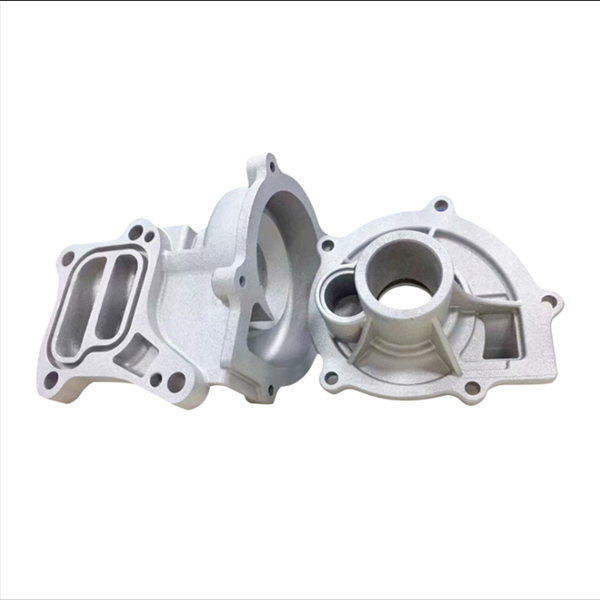
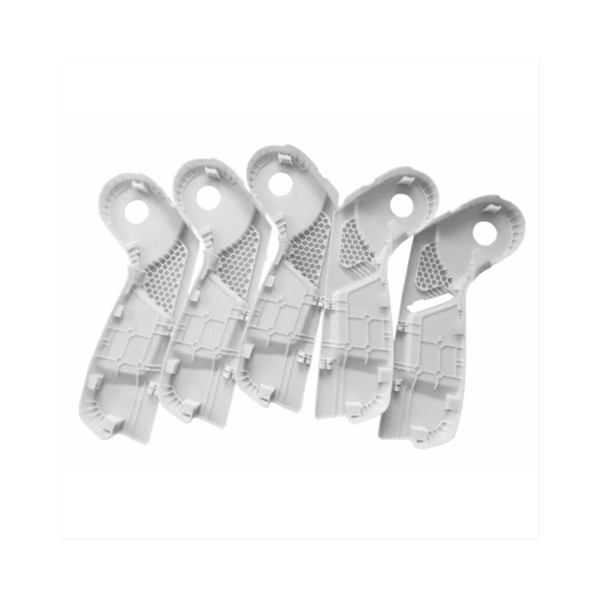
Metal 3D printing is ideal for creating fully functional prototypes and end-use parts.
Classification:
3D Printing
Keywords:
- metal 3d printing
- metal printing
- metal 3d printing service
- Description
- Specification
- Application
- FAQS
Metal materials 3D printing offers a versatile manufacturing solution by combining digital design freedom with the strength of metal alloys. This technology builds parts layer by layer from powdered metals, using methods such as laser sintering or melting, to achieve functional components with solid internal structures and detailed surface features.
The process supports a wide selection of metal materials, including stainless steel, titanium, aluminum, Inconel, and cobalt chrome. These alloys offer mechanical properties such as high strength, temperature resistance, corrosion resistance, and low weight, depending on the application. As a result, you can apply metal materials 3D printing to parts that need both structural performance and design complexity.
It is particularly effective for producing intricate geometries that are difficult or inefficient to machine conventionally. Internal channels, lattice structures, and topology-optimized designs can be manufactured without added tooling or part assembly. This flexibility can help reduce material usage while maintaining functional performance.
In addition to performance parts, the technology is often used for prototyping, design validation, and bridge production. You can produce parts in low volumes or custom batches without the delays and costs of mold making. This accelerates development timelines and supports faster iteration during the product design phase.
Post-processing techniques such as heat treatment, machining, surface smoothing, and coating further refine the mechanical properties or appearance of printed components. These steps help ensure that the final part meets your technical and aesthetic requirements.
Industries such as aerospace, automotive, robotics, medical devices, and consumer electronics benefit from this method. Whether the goal is to reduce part weight, combine multiple components into one, or respond quickly to changing design needs, this approach provides a practical solution.
By using metal-based additive manufacturing, you can expand design options, shorten production cycles, and explore new possibilities in functional part production.
| Parameter | Value / Description |
|---|---|
| Printing Technology | DMLS (Direct Metal Laser Sintering), SLM (Selective Laser Melting), EBM (Electron Beam Melting) |
| Layer Thickness | 20 µm – 100 µm |
| Lead Time | 1 – 7 days |
- Aerospace:Production of lightweight, high-strength parts for aircraft, engines, and spacecraft, such as brackets, turbine blades, and custom components.
- Automotive:Creation of complex, customized parts for vehicles, including engine components, exhaust systems, and performance parts for motorsport.
- Medical Devices:Manufacturing of personalized implants, surgical instruments, and prosthetics, tailored to individual patients' needs for better functionality and comfort.
- Tooling:Production of custom tools, jigs, fixtures, and molds, offering faster design iterations and reduced tooling costs.
- Industrial Applications:Creation of functional parts for industrial machinery, such as pumps, valves, and heat exchangers, with complex internal structures for better performance.
- Prototyping and R&D:Rapid prototyping of metal parts for testing and design verification, helping to quickly iterate and optimize product designs.
1. What is metal 3D printing?
Metal 3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a process where metal parts are created layer by layer from a digital model, using advanced technologies such as DMLS, SLM, or EBM.
2. What materials are used in metal 3D printing?
Common materials include titanium alloys (Ti-6Al-4V), stainless steel (316L, 17-4PH), aluminum alloys, Inconel, and cobalt-chrome, which offer a combination of strength, heat resistance, and durability.
3. What are the advantages of metal 3D printing?
It allows for the creation of complex geometries, reduces material waste, and eliminates the need for tooling, making it ideal for custom, low-volume production and rapid prototyping.
4. How strong are parts produced using metal 3D printing?
Metal 3D printed parts can have tensile strength ranging from 500 MPa to 1,200 MPa, depending on the material used, and are suitable for high-performance applications.
5. Can metal 3D printing be used for mass production?
While metal 3D printing is cost-effective for low-volume production and prototyping, it is generally not suited for mass production due to higher costs compared to traditional methods.